Basics in Chemical Bonding
Chemical Bond
Chemical bonds are permanent links between atoms or ions that enable them to form structures such as molecules, crystals, etc.
Chemical bonds are caused by forces that attract and stabilize the constituent elements.
Octet Rule
This is a rule that if observed for every chemical bond where the valence or outer shell of electrons of an element should satisfy a number of 8 through bonding.
Types of bond
Covalent
Covalent bonds are bonds that can be described as a sharing of valence electrons to satisfy the octet rule.
This bond occurs between two nonmetals.
Ionic
Ionic bonds are described as the giving and taking of valence electrons to satisfy the octet rule.
This bond occurs between a nonmetal and a metal, where the nonmetal receive the electron and becomes an anion and the metal loses an electron and become a cation.
Metallic
These are bonds that occur between two metals; and usually is formed because the valence electrons freely move from on atom to the other, without necessarily taking or sharing them.
Lewis Symbols and Structure
Valence Electrons
These are the electrons that are involved in the formation of bonds between atoms.
Lewis Electron-Dot Structure
A simplified representation of the valence electrons of an element.
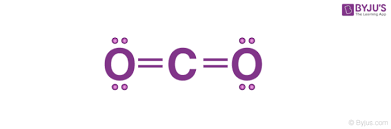
Changes in Matter
Physical Change
These are changes to the substances appearance.
Chemical
These are changes to the substances chemical composition.
Nuclear
These are changes to the substances nucleus.
Patterns in Chemical Reactivity
Combination
These are reactions where 2 or more substances ( Ex. and ) react to form a single substance ( Ex. ).
Decomposition
Often described as “Inverse Combination”, this involves the substance ( Ex. ) reacting to form 2 or more substances ( Ex. and ).
Combustion
Combustion reactions are rapid reactions that produce a flame, and commonly involve oxygen ( ) as a reactant.
Single Displacement
This reaction involves one part of a reactant being displaced onto the other reactant.
Double Displacement
This reaction involves where one part of each reactant compounds are displaced.
Oxidation
This involves the addition of oxygen ( ) and the removal of Hydrogen ( ).
Reduction
This reaction is the reversal of the oxidation reaction. The removal of oxygen ( ) and the addition of Hydrogen ( ).
Red-Ox Reaction
This reaction is the simultaneous oxidation and reduction of the reactants.
Neutralization
These are reactions between acids and bases, which are highly reactive.
Reactions Based on Energy
Endothermic
These are reactions that involves the absorption of heat and/or energy; it often makes the surroundings colder.
Exothermic
These are reactions that involve the release of heat and/or energy; it often makes the surroundings hotter.