What is Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is defined as the relationship between the relative quantities of substances taking part in a reaction or forming a compound, typically a ratio of whole integers.
In simple terms, it is the proportions in which specific elements and/or compounds react with one another.
Solving for the Values of a Chemical Reaction
When solving for values of measurements in a chemical reactions, there are two ways to do so; for both methods one must be mindful of the term STP.
STP, stands for Standard Temperature and Pressure. When one is told to assume STP, this means all values not explicitly given a value will get their corresponding values below
- Pressure () -
- Temperature () -
It is usual to have an understanding and to be familiar with the web of conversions shown below.
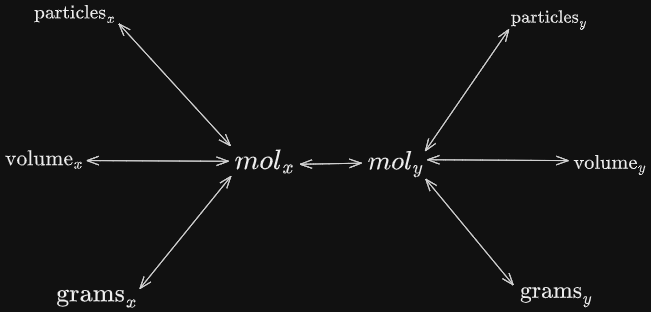
This web of conversion allows us to visualize the indirect links between units of our reactants and products. Through this web, we can see the conversions we have to conduct in order to get our desired value.
Usually, we first need to draw a path from our given value ( ex. the grams of our reactant, ) to our desired value ( ex. the volume of our product, ). This will give us an outline of our conversion process.
After this step, we then decide on which method we use to get our desired value. We have a choice between the Formula Method and Dimensional Analysis.
Via Formula Method
This method uses formulas for each step in the conversion. It is easy to digest but takes longer to solve.
Each step in our conversion will use the appropriate formula from the collection given below:
^7a9279Grams to Moles Conversion Formula
Link to original
- Use case:
- When converting from grams of the element to moles of the element , and the molecular weight of the element is given.
- Variables:
- - Moles of element ( )
- - Molecular weight of element ( )
- - Grams of element ( )
- Formula:
Transclude of Formulas#moles-to-grams
Volume to Moles Conversion Formula
Link to original
- Use case:
- When converting from volume of the element to moles of the element , and the temperature and pressure is given or is assumed as STP.
- Variables:
- - Moles of element ( )
- - Pressure ( ) { STP: }
- - Volume of element ( )
- - Gas constant ( )
- - Temperature ( ) { STP: }
- Formula:
^ebc0b9Moles to Volume Conversion Formula
Link to original
- Use case:
- When converting from moles of the element to volume of the element , and the temperature and pressure is given or is assumed as STP.
- Variables:
- - Volume of element ( )
- - Moles of element ( )
- - Gas constant ( )
- - Temperature ( ) { STP: }
- - Pressure ( ) { STP: }
- Formula:
Number of Particles to Moles Conversion Formula
Link to original
- Use case:
- When converting from number of particles of the element to moles of the element , and the temperature and pressure is given or is assumed as STP.
- Variables:
- - Number of moles of element ( )
- - Number of atoms of a given element
- - Avogadro’s Number ().
- Formula:
Moles to Number of Particles Conversion Formula
Link to original
- Use case:
- When converting from number of particles of the element to moles of the element , and the temperature and pressure is given or is assumed as STP.
- Variables:
- - Number of atoms of a given element
- - Number of moles of element ( )
- - Avogadro’s Number ().
- Formula:
^dc5febMole Conversion Between Different Molecules Formula
Link to original
- Use case:
- When converting from the moles of element to moles of element and a balanced chemical equation is given.
- Variables:
- - Coefficient of element in the balanced chemical equation ( )
- - Coefficient of element in the balanced chemical equation ( )
- Formula:
If we were to use the formula method on our previous example, we would use the following formulas in this order:
Via Dimensional Analysis
This method has no set formula and relies on the analysis of the units and their proportions to get the final answer. Ideal for efficiency but requires extra effort in the formulation.
Reinterpreting Derived Units
Derived units can be expressed in a compact form but it can be reinterpreted as a relationship or a fraction.
Derived units are often use as Conversion Factors
Conversion Factors
Conversion factors are a fractional value that represents the proportional relationship between two units.
In conversion, your given unit would be the unit of your conversion factor’s denominator, and your desired unit would be the unit of your conversion factor’s numerator.
Below is the gram to mole conversion factor for water.
Below are the conversion factors commonly used dimensional analysis:
Legend:
-
- Molecular weight of element .
-
- Pressure of element . ( equal to when assuming STP )
-
- Volume of element .
-
- Temperature of element . ( equal to when assuming STP )
-
- Number of moles of element .
-
- Gas constant ( )
-
- Avogadro’s Number ().
-
- Coefficient of element .
-
- Coefficient of element .
-
Mole to grams
- Grams to mole
- Mole to volume
- Volume to mole
- Particles to mole
- Mole to particle
- Mole to mole
Note: When choosing a conversion factor, remember that your desired unit is the numerator, and your given unit is the denominator.
Dimensional Analysis Process
Solving using dimensional analysis involves multiplying the given value with all the conversion factors that fit the outline.
If we were to use dimensional analysis on our previous example, our formula would look like this: