What is a Redox Reaction
An oxidation–reduction or redox reaction is a reaction that involves the transfer of electrons between chemical species (the atoms, ions, or molecules involved in the reaction).
It is composed of two reactions occurring simultaneously; the reactions in question are the: reduction reaction and oxidation reaction.
Redox reactions are in processes present in every day life, such as the burning of fuels, corrosion of metals, and even the process of photosynthesis.
Process of a Redox Reaction
During a redox reaction, some species undergo oxidation, or the loss of electrons; while others undergo reduction, or the gain of electrons.
In this given reaction ( the rusting of iron ):
We can observe the following:
- in the left hand side: has an oxidation state of because it is not bonded to anything;
- also in the left hand side: has an oxidation state of because it is not bonded to anything;
- on the right hand side: has an oxidation state of through the criss-cross method;
- also on the right hand side: has an oxidation state of through the criss-cross method;
This brings us to the conclusion that is oxidized and is reduced.
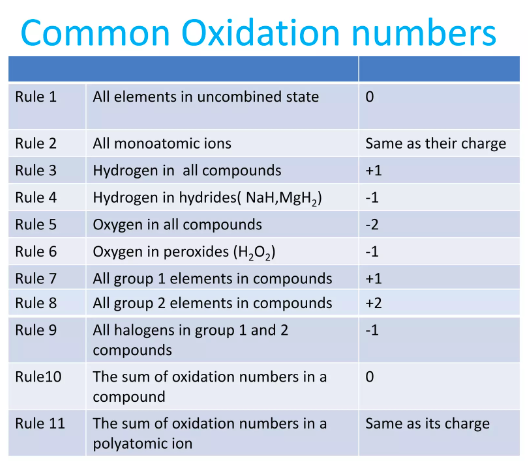
Oxidation Numbers
Oxidation numbers or oxidation states are the key sign that identifies which species are oxidants and reductant.
Key Definitions
- Reduction
- a reaction that involves the gaining of electrons;
- Oxidation
- a reaction that involves the losing of electrons;
- Redox
- a simultaneous reaction of reduction and oxidation;
- Oxidation States
- the number that describes the degree of oxidation an atom has in a chemical compound;
- it is written as a superscript; and denotes the subscript of the atom of polyatomic ion it is bonded with;
- Reductant
- the species that undergoes oxidation and encourages reduction;
- Oxidant
- the species that undergoes reduction and encourages oxidation;
- monoatomic ions
- ions that consist of only one element;