According to Periodic Law, arranging our elements in increasing atomic number ( like how it is arranged in the Periodic Table ), we begin to see patterns in the elemental characteristics, that is called a Periodic Trend.
Blocks
Blocks are sections of the periodic table that share the same orbitals their valence electrons orbit.
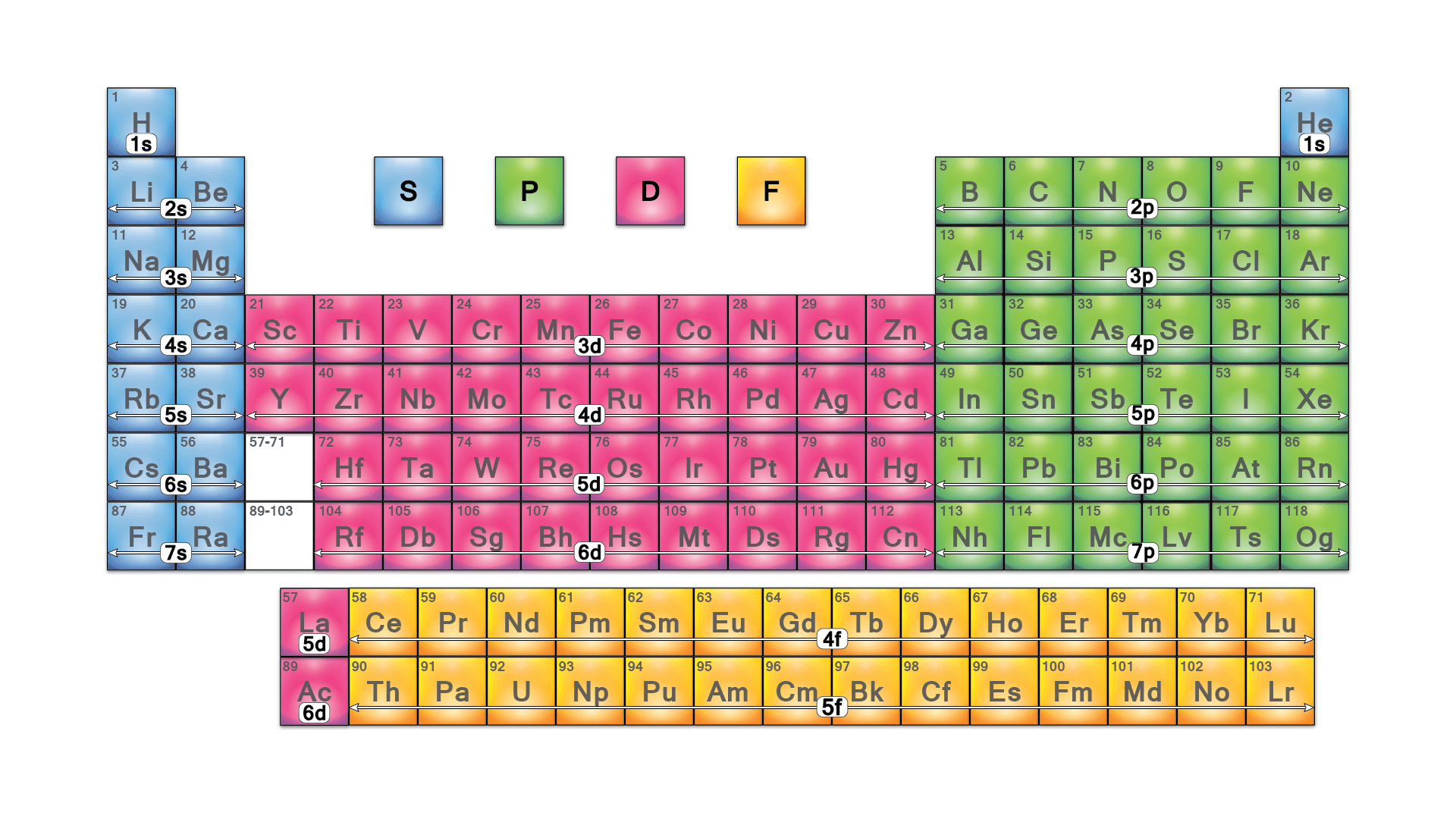
- S Block
- These are elements that share the s orbital as their valence electron orbital.
- P Block
- These are elements that share the p orbital as their valence electron orbital.
- D Block
- These are elements that share the d orbital as their valence electron orbital.
- F Block
- These are elements that share the f orbital as their valence electron orbital.s
Group A vs Group B
Groups are divided into two groups; group A, the representative elements; and group B, the transition elements.
Representative elements are often found in the S block and P block, whereas the transition elements are found in the D and F blocks.
Periodic Trends
Electronegativity
Electronegativity is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons when forming a chemical bond.
The difference in electronegativity between two elements in a bond will determine its type of bond and its strength.
| Type of Bond | Difference in Electronegativity |
|---|---|
| Non-Polar Covalent | |
| Polar Covalent | |
| Ionic Bonds |
Electronegativity increases as you move from left to right ( ) and as you move up a group ( ).
Ionization Energy
Ionization Energy is the amount of energy that is required to remove a valence electron from an isolated atom in a gaseous state.
Ionization Energy increases as you move from left to right ( ) and as you move up a group ( ).
Electron Affinity
Electron Affinity is the tendency to more easily accept electrons and form negative ions or anions.
Electron Affinity increases as you move from left to right ( ) and as you move up a group ( ).
Atomic Radius
Atomic Radius is the total distance from the nucleus of an atom to the outmost orbital of its electrons.
Atomic radius increases you move right to left ( ) and as move down a group ( ). Metallic Character Metallic Character is the tendency to lose an electron in a bond and form positive ions or cations.
Metallic Character increases as you move from right to left ( ) and as you move down a group ( ).
Three Elemental Type
Metals
Metals are elements in the periodic table that have the tendency to lose electrons and be great conductors of heat and electricity.
The traits of metals are the following:
- Form cations (lose electron/s)
- Metallic luster
- Good conductors (heat and electricity)
- Malleable and ductile
- High melting point
- Solid at room temperature
Non Metals
Nonmetals are elements in the periodic table that have the tendency to gain electrons and form anions.
The traits of nonmetals are the following:
- Form anions (gain electron/s)
- Not metallic
- Brittle as solids
- Good insulators
- Low melting point
- Can be solid, liquid, or gas
Metalloids
These are elements whose properties are intermediate between those of metals and solid nonmetals